Minimally Invasive Surgery At Medicsi
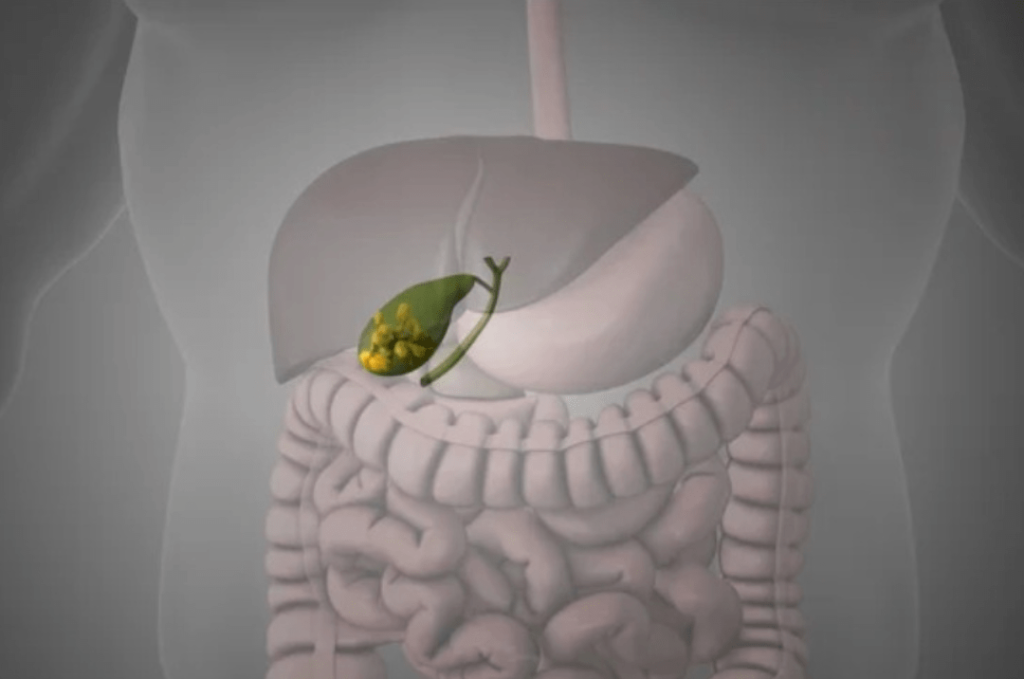
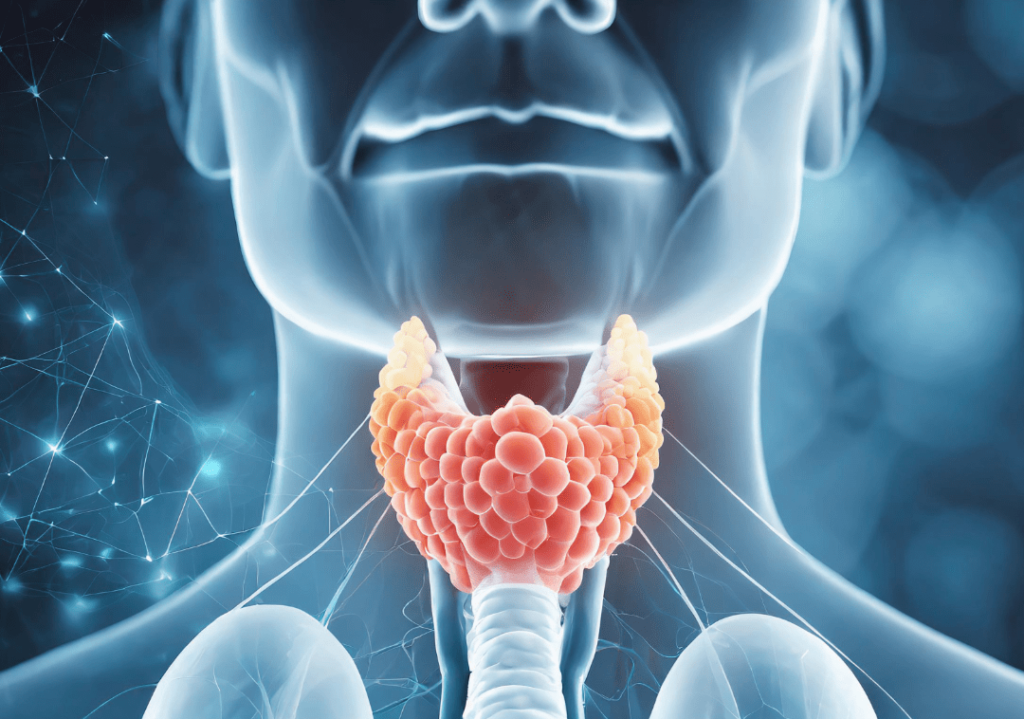
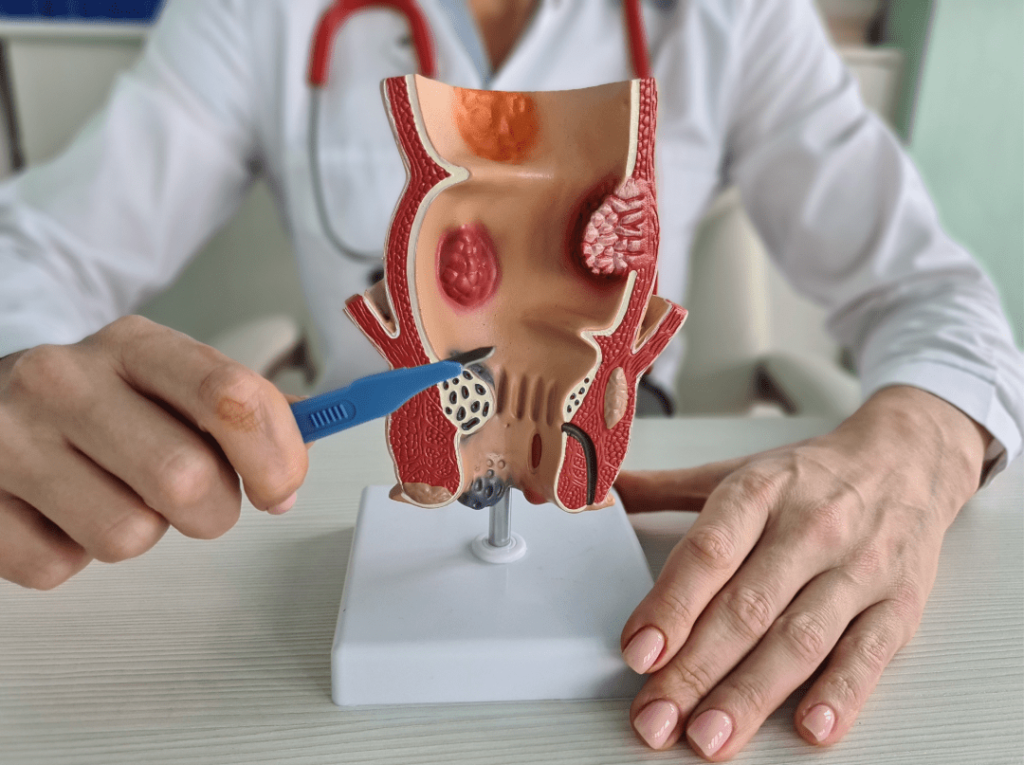
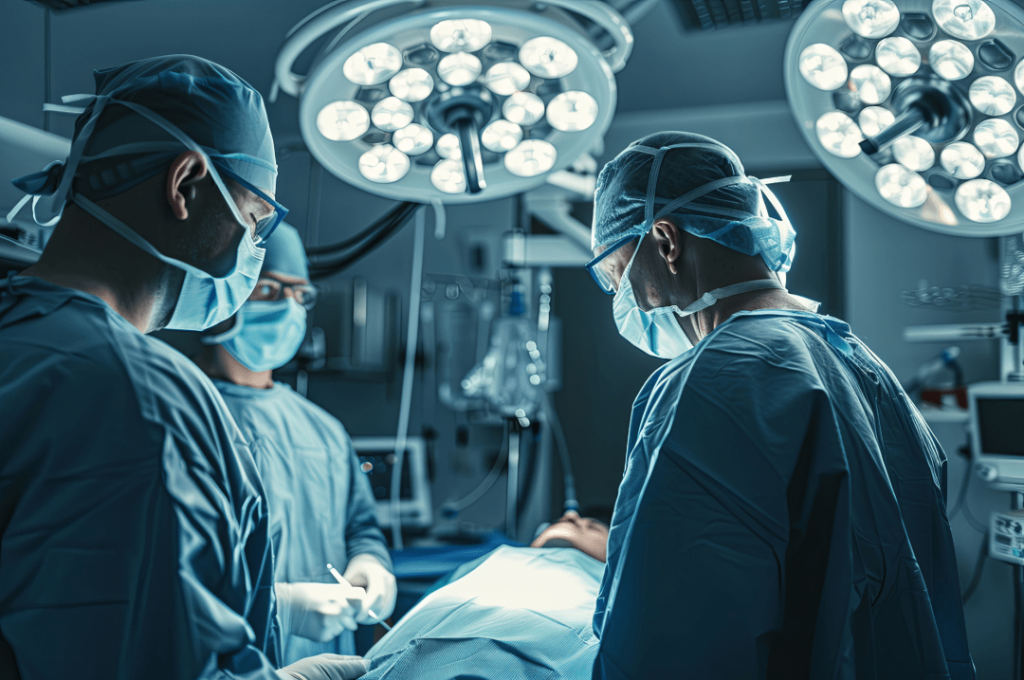
Patient Information Blogs Minimally Invasive Surgery At Medicsi Courtesy of: Dr. Reem Shahid; Sen. Reg., Medicsi 07/06/2024 Minimally Invasive Surgery At Medicsi Courtesy of: Dr. Reem Shahid; Sen. Reg., Medicsi 07/06/2024 Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) came about in the 1980s as a safe way to meet surgical needs. In recent years, minimally invasive surgery (MIS) has revolutionised the field of surgery, offering patients less pain, faster recovery times, and fewer complications compared to traditional open surgery. Since then, the use of minimally invasive surgery has spread widely in many surgical areas, including abdominal, pelvic, and lung surgery, etc. Here at Medicsi, we believe it is essential to raise public awareness about the benefits and the awareness of this remarkable approach to surgical care. What is Minimally Invasive Surgery? Minimally invasive surgery, also known as laparoscopic or keyhole surgery, involves performing operations through small incisions using specialised instruments and a camera. The camera sends live video to a monitor / TV screen in front of the surgeons, which allows them to visualise the anatomy as they perform complex surgeries with minimal trauma to the patient. This technique contrasts sharply with traditional open surgery, which requires larger incisions to access the area of concern. Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) came about in the 1980s as a safe way to meet surgical needs. In recent years, minimally invasive surgery (MIS) has revolutionised the field of surgery, offering patients less pain, faster recovery times, and fewer complications compared to traditional open surgery. Since then, the use of minimally invasive surgery has spread widely in many surgical areas, including abdominal, pelvic, and lung surgery, etc. Here at Medicsi, we believe it is essential to raise public awareness about the benefits and the awareness of this remarkable approach to surgical care. What is Minimally Invasive Surgery? Minimally invasive surgery, also known as laparoscopic or keyhole surgery, involves performing operations through small incisions using specialised instruments and a camera. The camera sends live video to a monitor / TV screen in front of the surgeons, which allows them to visualise the anatomy as they perform complex surgeries with minimal trauma to the patient. This technique contrasts sharply with traditional open surgery, which requires larger incisions to access the area of concern. Key Advantages of Minimally Invasive Surgery Reduced Pain and Discomfort Smaller incisions mean less trauma to the body, resulting in significantly reduced postoperative pain and discomfort. This often translates to a decreased need for pain medication. Faster Recovery Times Patients undergoing MIS typically experience quicker recovery periods. They can return to their normal activities and work sooner compared to those who have had traditional open surgery. Shorter Hospital Stays The reduced trauma and faster recovery associated with MIS often lead to shorter hospital stays, allowing patients to return home sooner and lowering overall healthcare costs. Lower Risk of Complications Minimally invasive techniques are associated with a lower risk of infections and other complications. The precision of these procedures minimises damage to surrounding tissues and reduces blood loss during surgery. Smaller Scars The small incisions used in MIS result in smaller, less noticeable scars, which can be an important consideration for many patients, especially when the surgery involves visible areas of the body. Common Procedures Performed with Minimally Invasive Surgery Minimally invasive techniques are now widely used for various types of surgeries worldwide. Below-mentioned surgeries are currently being done here at Medicsi. Abdominal Surgeries Gallbladder Resection (Cholecystectomy) and Appendicectomy Hernia Repair Gastric Surgery, like Gastric bypass. Colorectal procedures, including cancer resections, can be performed using MIS, improving outcomes and reducing complications. Gynaecological Surgeries Ovarian Cystectomy Endometriosis Surgery Ectopic Pregnancy Tubal Ligations Myomectomies Hysterectomies Intrauterine Surgeries Pelvic Organ Prolapse Repairs The following minimally invasive procedures will be introduced soon at Medicsi: Vascular Surgery Endovascular Aneurysm Repair Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT): Treatment of varicose veins using laser energy to close off the affected veins. Gastro-Intestinal Surgeries Neurosurgery Orthopaedic Surgery Arthroscopy Minimally Invasive Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Thoracic Surgery Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): Treatment of lung conditions, such as lobectomy for lung cancer, pleural effusion drainage, and biopsy, using a thoracoscope. Minimally invasive esophagectomy Minimally invasive thymectomy Thoracoscopic sympathectomy Urological Surgery Laparoscopic nephrectomy Laparoscopic prostatectomy Ureteroscopy Percutaneous nephrolithotomy Transurethral resection of prostate Ent Surgery Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Septoplasty Endoscopic Laryngeal Surgery Endoscopic Ear Surgery Balloon Sinuplasty If you or a loved one are facing the possibility of undergoing surgery, Medicsi encourages you to discuss minimally invasive options with your consultant. Understanding the benefits and possibilities of MIS can help you make informed decisions about your surgical options. Key Advantages of Minimally Invasive Surgery Reduced Pain and Discomfort Smaller incisions mean less trauma to the body, resulting in significantly reduced postoperative pain and discomfort. This often translates to a decreased need for pain medication. Faster Recovery Times Patients undergoing MIS typically experience quicker recovery periods. They can return to their normal activities and work sooner compared to those who have had traditional open surgery. Shorter Hospital Stays The reduced trauma and faster recovery associated with MIS often lead to shorter hospital stays, allowing patients to return home sooner and lowering overall healthcare costs. Lower Risk of Complications Minimally invasive techniques are associated with a lower risk of infections and other complications. The precision of these procedures minimises damage to surrounding tissues and reduces blood loss during surgery. Smaller Scars The small incisions used in MIS result in smaller, less noticeable scars, which can be an important consideration for many patients, especially when the surgery involves visible areas of the body. Common Procedures Performed with Minimally Invasive Surgery Minimally invasive techniques are now widely used for various types of surgeries worldwide. Below-mentioned surgeries are currently being done here at Medicsi. Abdominal Surgeries Gallbladder Resection (Cholecystectomy) and Appendicectomy Hernia Repair Gastric Surgery, like Gastric bypass. Colorectal procedures, including cancer resections, can be performed using MIS, improving outcomes and reducing complications. Gynaecological Surgeries Ovarian Cystectomy Endometriosis Surgery Ectopic Pregnancy Tubal Ligations Myomectomies Hysterectomies Intrauterine Surgeries
Minimally Invasive Surgery At Medicsi Read More »