Navigating Gall Stones
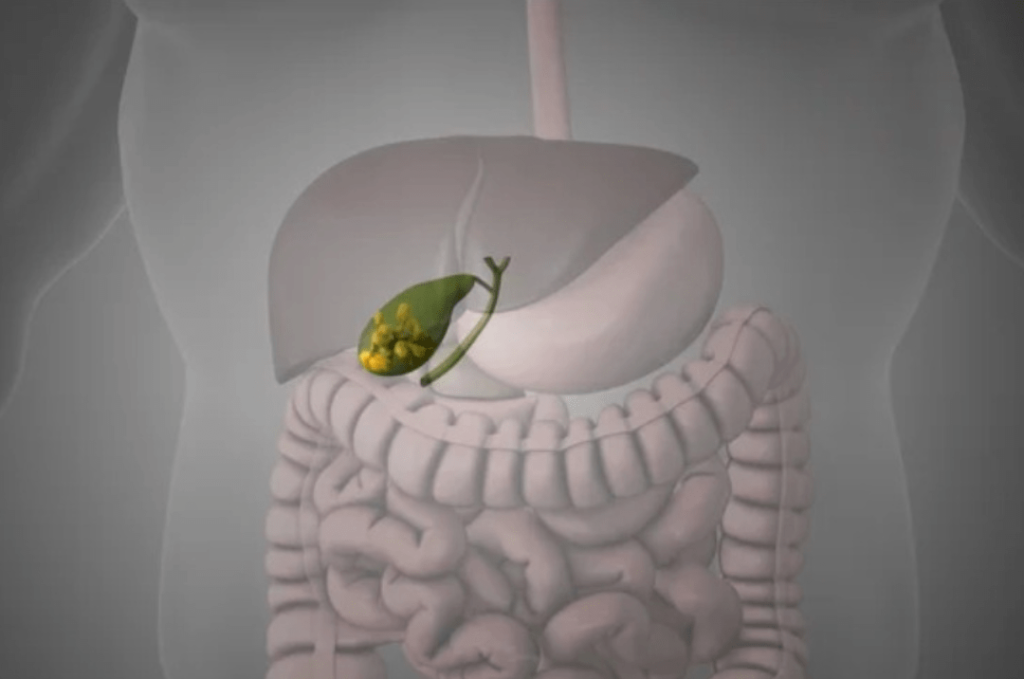
Patient Information Blogs Navigating Gall Stones Courtesy of: Dr. Adeel Jatala; Senior Reg., Medicsi 06/05/2024 Navigating Gall Stones Courtesy of: Dr. Adeel Jatala; Senior Reg., Medicsi 06/05/2024 Guide for Everyday Understanding Gallstones, those trouble-making little formations in the gallbladder, can cause significant discomfort and potential complications if left untreated. But fear not! Understanding gallstones, their symptoms, and the necessary investigations can empower you to take control of your health effectively. What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are deposits that form in the gallbladder either from cholesterol or bile salts. The gallbladder's main function is to store bile. When you eat, the gallbladder releases bile into the small intestine to aid in the digestion of fats. Gallstones can vary in size and number from single to multiple. Causes of Gallstones: The exact cause of gallstones is not always clear, but they often develop when there is an imbalance in the substances that make up bile. Factors that can increase the risk of gallstones include: Being Overweight or Obese: Excess weight can increase the amount of cholesterol in bile, which can lead to the formation of gallstones. Rapid Weight Loss: Losing weight too quickly can also contribute to the formation of gallstones. Certain Diets: Diets high in fat and cholesterol and low in fibre can increase the risk of gallstones. Family History: If someone in your family has had gallstones, you may be more likely to develop them too. Other comorbidities: Conditions such as diabetes and liver disease can increase the risk of gallstones. Common Symptoms of Gallstones: Gallstones don't always cause symptoms, but when they do, the symptoms can be quite painful. Common symptoms of gallstones include: Sudden and Intense Pain (Biliary colic): This pain, known as gallbladder colic, typically occurs in the upper abdomen and can last for several hours. Nausea and Vomiting: Some people may experience nausea and vomiting along with the pain. Jaundice: If not treated timely a gallstone blocks the bile duct, which can lead to jaundice, a condition characterised by yellowing of the skin and eyes. Fever: In some cases, gallstones can cause inflammation of the gallbladder, leading to fever and chills. It can complicate serious conditions like pancreatitis. What are the management options for gallstones? If you're experiencing symptoms of gallstones, it's important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis. It's very important to understand that not all gallbladder stones are operated on. If you have severe symptoms or complications, such as gallbladder inflammation or blockage of the bile ducts, there are some surgical options to remove the gallbladder. Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. Most preferred these days due to its advantages like less pain and a short stay in the hospital. Open cholecystectomy: Only done if the laparoscopic one is not available or possible. A discussion with your surgeon will clarify the reasons further. Guide for Everyday Understanding Gallstones, those trouble-making little formations in the gallbladder, can cause significant discomfort and potential complications if left untreated. But fear not! Understanding gallstones, their symptoms, and the necessary investigations can empower you to take control of your health effectively. What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are deposits that form in the gallbladder either from cholesterol or bile salts. The gallbladder's main function is to store bile. When you eat, the gallbladder releases bile into the small intestine to aid in the digestion of fats. Gallstones can vary in size and number from single to multiple. Causes of Gallstones: The exact cause of gallstones is not always clear, but they often develop when there is an imbalance in the substances that make up bile. Factors that can increase the risk of gallstones include: Being Overweight or Obese: Excess weight can increase the amount of cholesterol in bile, which can lead to the formation of gallstones. Rapid Weight Loss: Losing weight too quickly can also contribute to the formation of gallstones. Certain Diets: Diets high in fat and cholesterol and low in fibre can increase the risk of gallstones. Family History: If someone in your family has had gallstones, you may be more likely to develop them too. Other comorbidities: Conditions such as diabetes and liver disease can increase the risk of gallstones. Common Symptoms of Gallstones: Gallstones don't always cause symptoms, but when they do, the symptoms can be quite painful. Common symptoms of gallstones include: Sudden and Intense Pain (Biliary colic): This pain, known as gallbladder colic, typically occurs in the upper abdomen and can last for several hours. Nausea and Vomiting: Some people may experience nausea and vomiting along with the pain. Jaundice: If not treated timely a gallstone blocks the bile duct, which can lead to jaundice, a condition characterised by yellowing of the skin and eyes. Fever: In some cases, gallstones can cause inflammation of the gallbladder, leading to fever and chills. It can complicate serious conditions like pancreatitis. What are the management options for gallstones? If you're experiencing symptoms of gallstones, it's important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis. It's very important to understand that not all gallbladder stones are operated on. If you have severe symptoms or complications, such as gallbladder inflammation or blockage of the bile ducts, there are some surgical options to remove the gallbladder. Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. Most preferred these days due to its advantages like less pain and a short stay in the hospital. Open cholecystectomy: Only done if the laparoscopic one is not available or possible. A discussion with your surgeon will clarify the reasons further. Recent Blogs edit post What is Medical Aesthetics Read More edit post Managing Your Pain Read More edit post PREMATURE MENOPAUSE: IT IS BEING DIAGNOSED TOO LATE Read More
Navigating Gall Stones Read More »